In larger income nations, environmentally friendly lifestyles, urban planning, land and water pollution cleanup, cat what’s up human cats love all over printed crocs and oil spills are continuing points at the forefront of public well being in collaboration with environmental and occupational well being safety agencies.
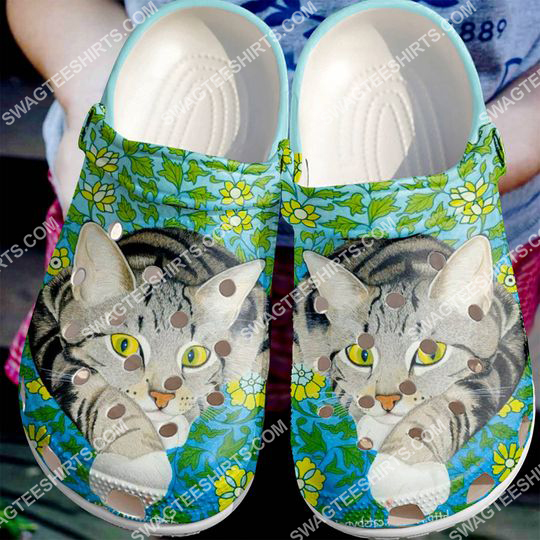
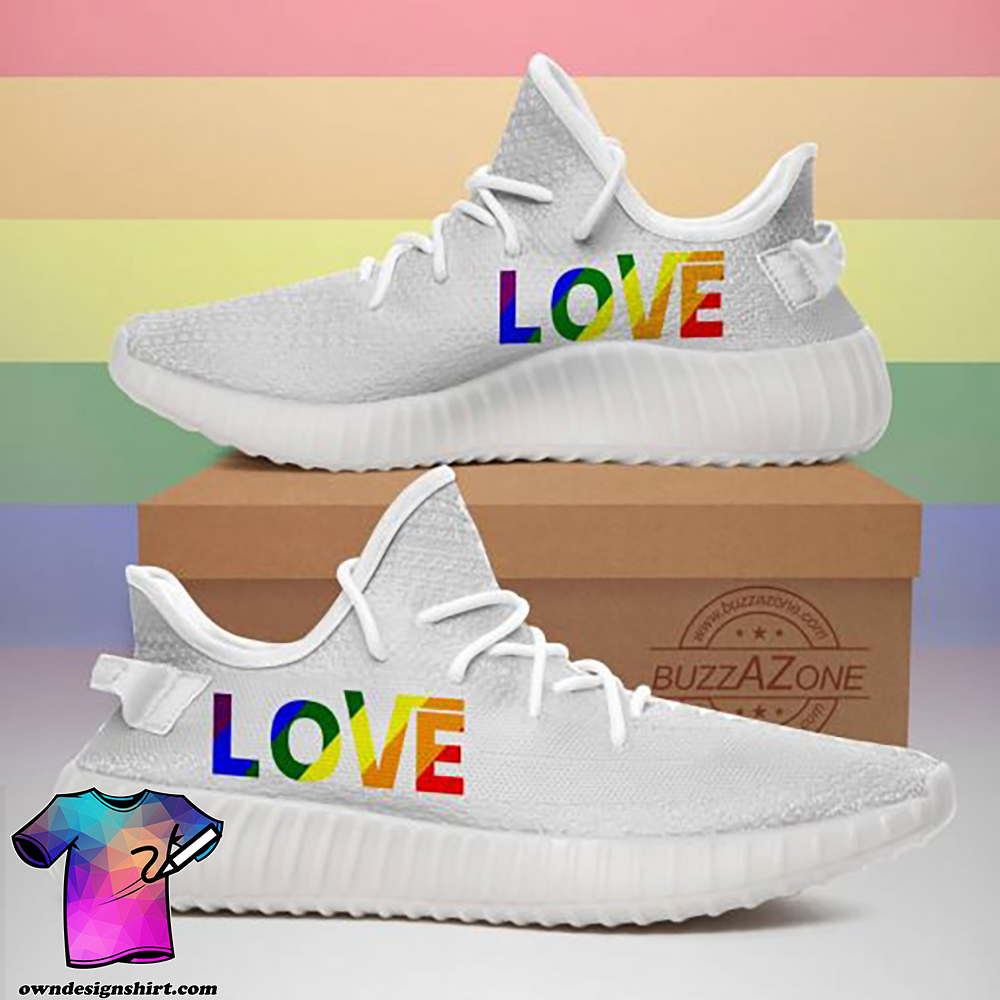
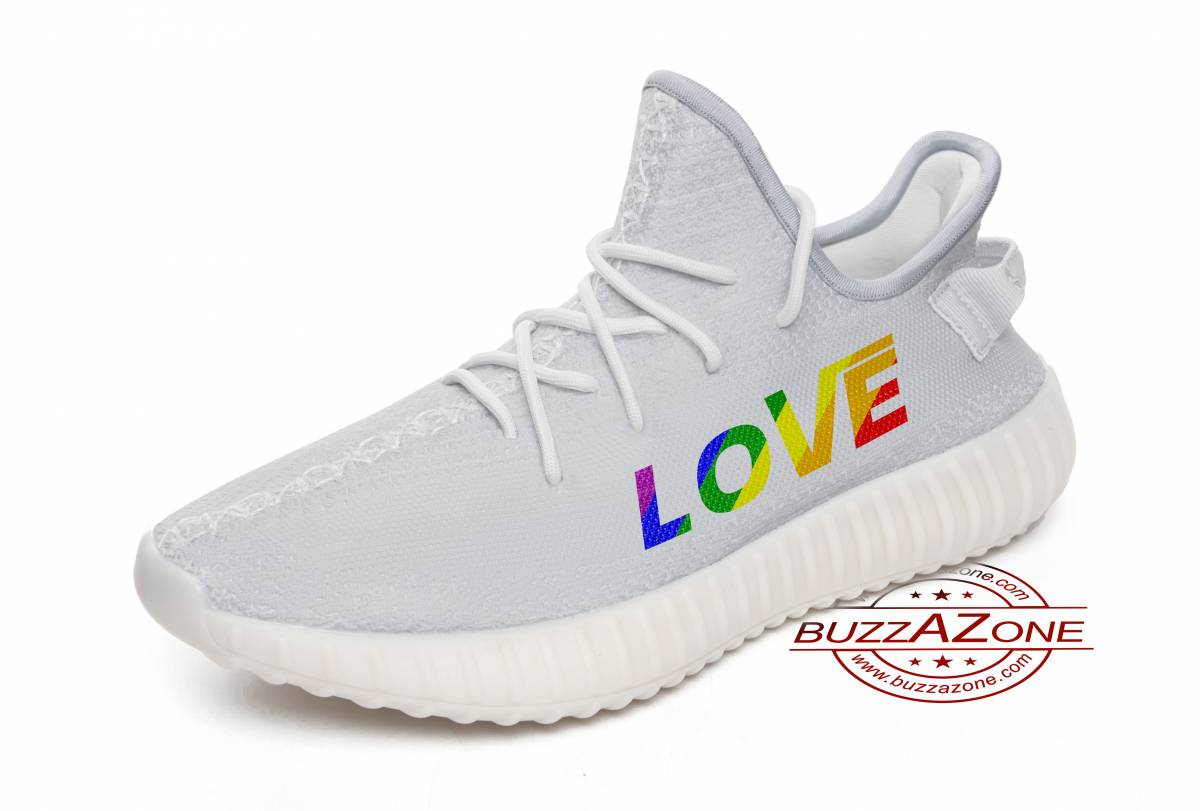
cat what’s up human cats love all over printed crocs
e to build an equal framework for temporal ecology. Climate change has directly pressed ecologists to understand and predict ecological dynamics in non-stationary environments, while also challenged elementary assumptions of many concepts, fashions and approaches. However, similarities between space and time, particularly associated problems with scaling, present an overview for bettering ecological fashions and forecasting of temporal dynamics, while the distinctive attributes of time, notably its emphasis on occasions and its singular direction, highlight the place new approaches are wanted. We emphasise how a renewed, interdisciplinary focus on time would coalesce associated ideas, assist develop new theories and methods and guide additional information assortment. The subsequent challenge shall be to unite predictive frameworks from spatial and temporal ecology to construct strong forecasts of when and the place environmental change will cat what’s up human cats love all over printed crocs pose the biggest threats to species and ecosystems, as well as figuring out the best alternatives for conservation. of considerable public well being significance on this region, particularly, malaria and irrigation; epidemic meningitis and land degradation; onchocerciasis and deforestation. We spotlight the confounding effect of climate variability, which acts as a driver of each land-use change and human health. We conclude, as have others, that the scale of observation at all times issues, and complicated and dynamic feedbacks among social-ecological systems aren’t easily teased apart. We recommend that in order to set up the causal chain of interactions between land-use change and human health outcomes two approaches are essential. The first is to have a radical understanding of the aetiology of disease and the specific mechanisms by which land-use and local weather variability affect the transmission of pathogens. This is achieved by focused, detailed studies encompassing a variety of potential drivers, that are inevitably small scale and sometimes cowl quick time periods.
The second consists of enormous-scale research of statistical associations between transmission indices or well being outcomes and environmental variables stratified by identified ecological or socio-financial confounders, and enough in measurement to beat native biases in results. Such research actions need to be designed to tell one another if we’re to develop predictive models for monitoring these illnesses and to develop built-in packages for human health and sustainable land use. ailments proceed to contribute significantly to the worldwide burden of disease, and trigger epidemics that disrupt well being safety and cause wider socioeconomic impacts all over the world. All are delicate in numerous ways to climate and local weather conditions, in order that the continuing tendencies of accelerating temperature and extra variable climate threaten to undermine recent world progress towards these ailments. Here, we review the current state of the global public well being effort to address this challenge, and description associated initiatives by the World Health Organization and its partners. Much of the controversy to date has centred on attribution of past changes in disease charges to climate change, and using scenario-based models to project future adjustments in threat for specific ailments. While these can give helpful indications, the unavoidable uncertainty in such analyses, and contingency on other socioeconomic and public health determinants in the past or future, restrict their utility as decision-help tools. For operational well being companies, essentially the most urgent want is the strengthening of present illness management efforts to deliver down present disease rates and handle brief-term climate risks, which can, in flip, improve resilience to long-term climate change. The WHO and associate companies are working by way of a range of programmes to make sure political help and financial investment in preventive and curative interventions to deliver down current illness burdens; promote a complete approach to climate risk management; help utilized analysis, through definition of worldwide and regional research agendas, and focused research initiatives on priority diseases and inhabitants teams. © The Author Published by the Royal Society. All rights reserved. Air pollution, climate change, deforestation, desertification, water shortages, and population progress, especially in low-income international locations, can lead to environmental and human tragedies on a vast scale.
Click to buy cat what’s up human cats love all over printed crocs and hope you like
See more in here
































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.